Targeting your audience by event payloads
Use Swrve’s new event payload targeting system to create more focused and refined campaign audiences. You might already target your users based on the count or recency of an event—for example, users who searched for a hotel at least three times or booked a flight in the last seven days. Event payload conditions add more granular criteria that users must meet to qualify for the target audience. For example, users who searched for a flight in the last seven days, where the destination airport was LAX and the number of travelers included children.
This article explains how to target your campaign audiences using behavioral event payloads and how the filters for various event data types work. It also provides several examples to help you learn how to use event payloads to create highly relevant, targeted audiences for all your campaigns.
Prerequisites
Configure events and payloads
To target your audience by event payloads, first configure the events and payloads you want to use for targeting purposes. For more information, see Configuring event payloads, or contact your CSM at support@swrve.com for further assistance. They will work with you to define the best schema for the events and payloads you want to use to target your users.
Examples of payload targeting
The Custom Audience tab in the audience builder has separate sections for User Profile filters (criteria that is based on user, device, or event profiles) and User Behavior filters (filters based on historical user behavior). The User Behavior section includes the option to specify additional payload criteria with the recency and frequency of an event. The following examples show how to use payload targeting with user profile filters to build your audiences.
Media and entertainment
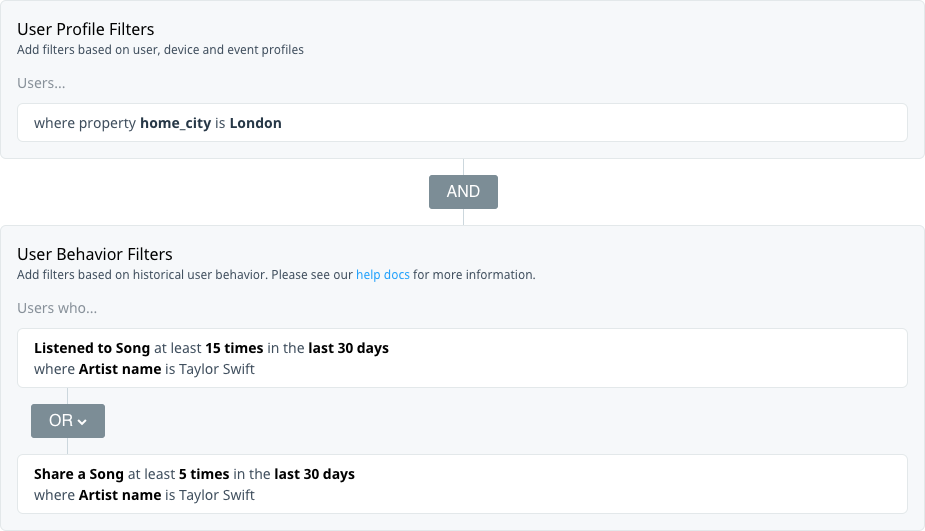
Target your audience based on their artist listening or sharing preferences to promote an upcoming concert in the area.
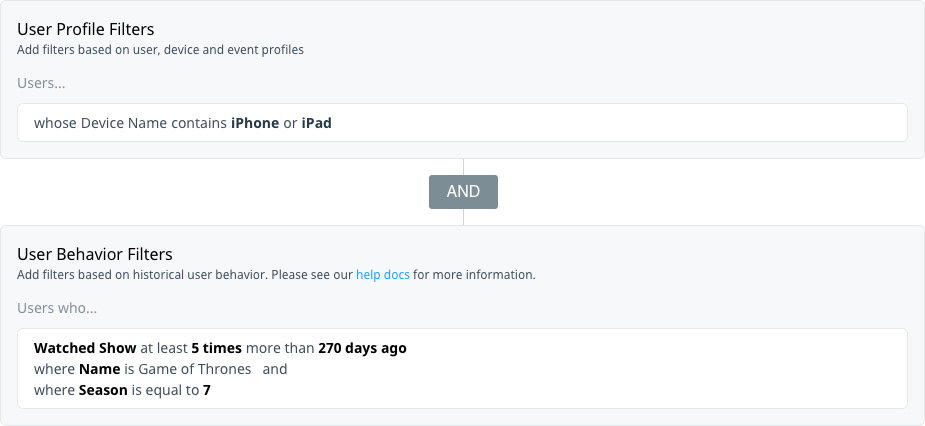
Target users who watched the previous season of a program on their mobile device or tablet to promote an upcoming season or premium subscription service.
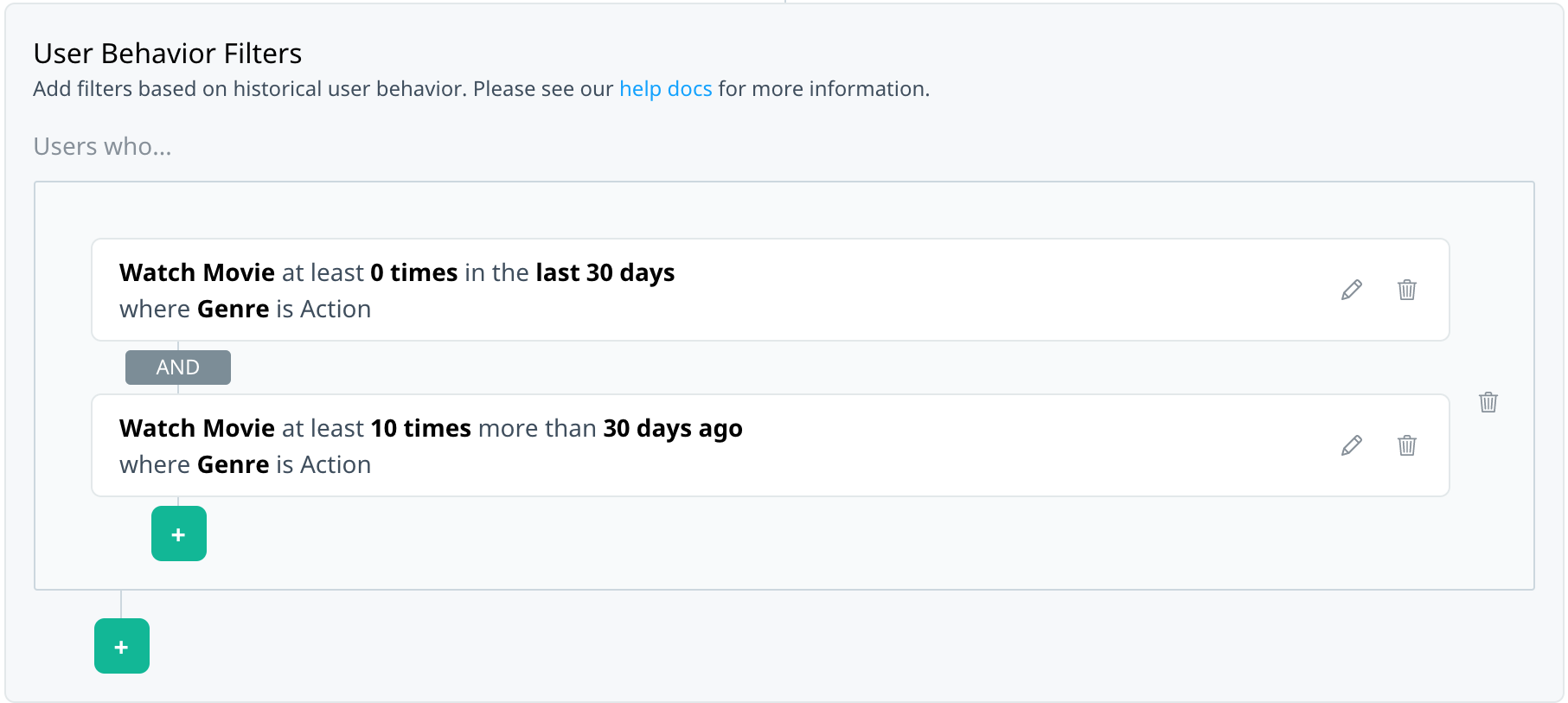
Target users who haven’t watched their favorite movie genre recently.
Travel
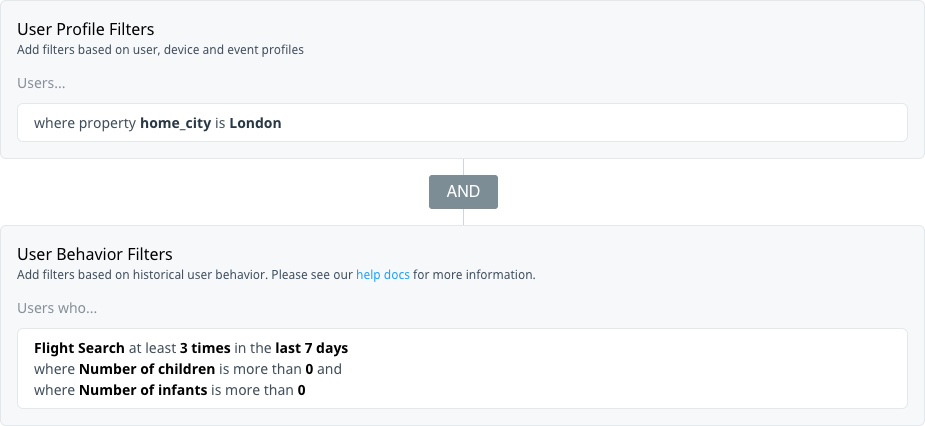
Target users from a specific departure city who searched for flights that included children in the number of travellers to promote family-friendly vacation packages.
Retail
Target users who viewed certain sale items, by category, to promote a seasonal sale.
Finance
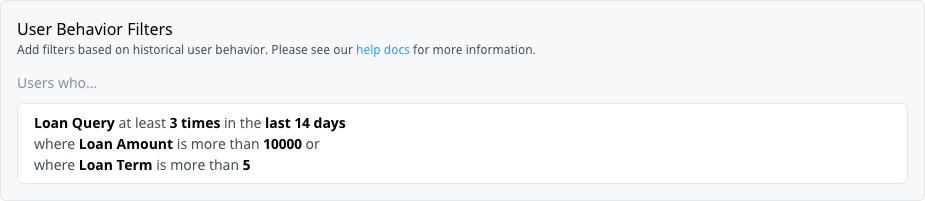
Target users who made recent loan queries above a certain amount or for a longer term to promote additional services.
User behavior filters
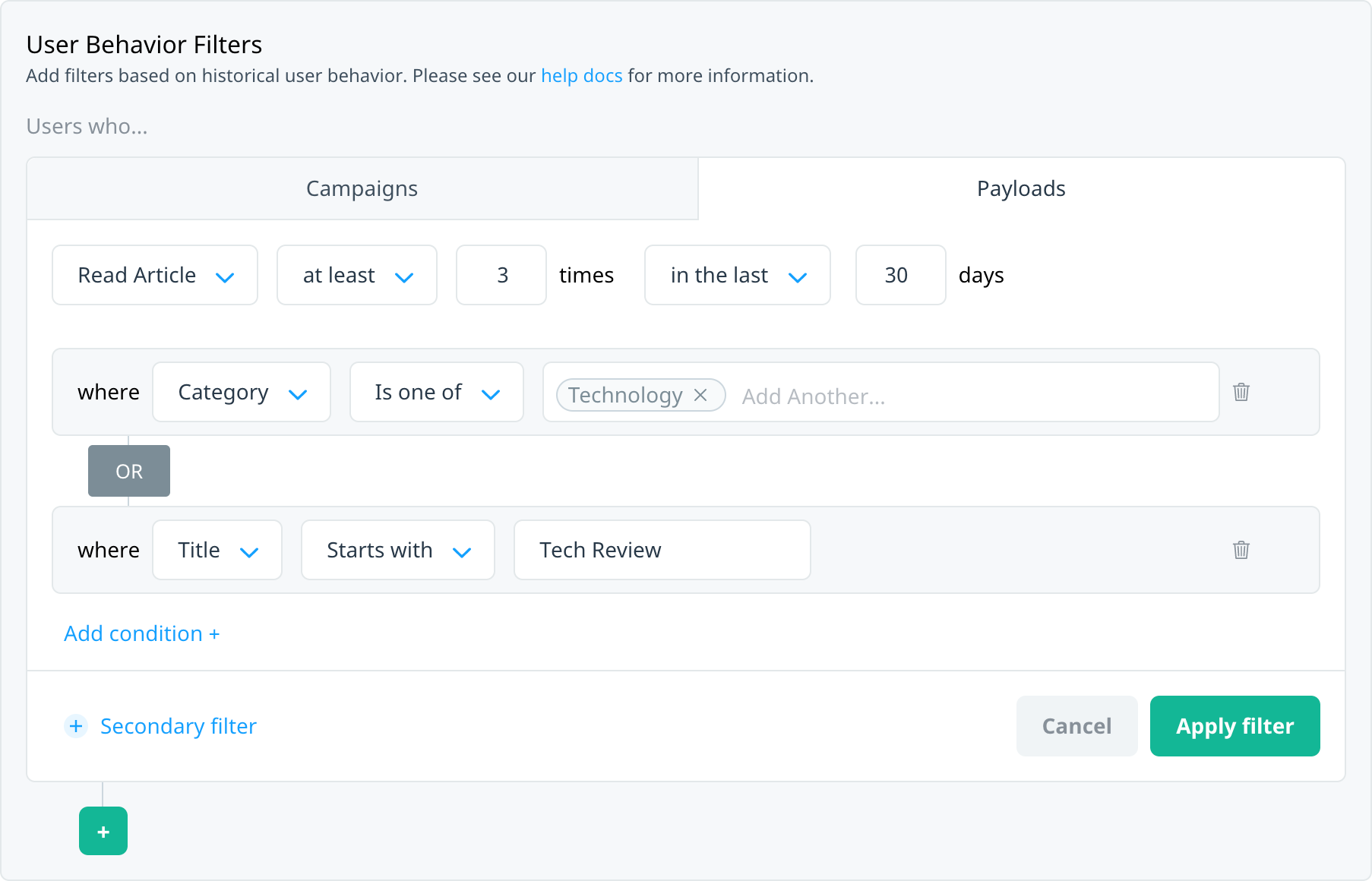
To successfully target your audience using payload criteria, it’s important to understand how the filters and options available work together to make an audience. To access User Behavior filters, on the Audience screen (or Define Target Audience step of in-app message and Conversation campaigns), select Custom Audience, and then under User Behavior Filters, select Payloads.
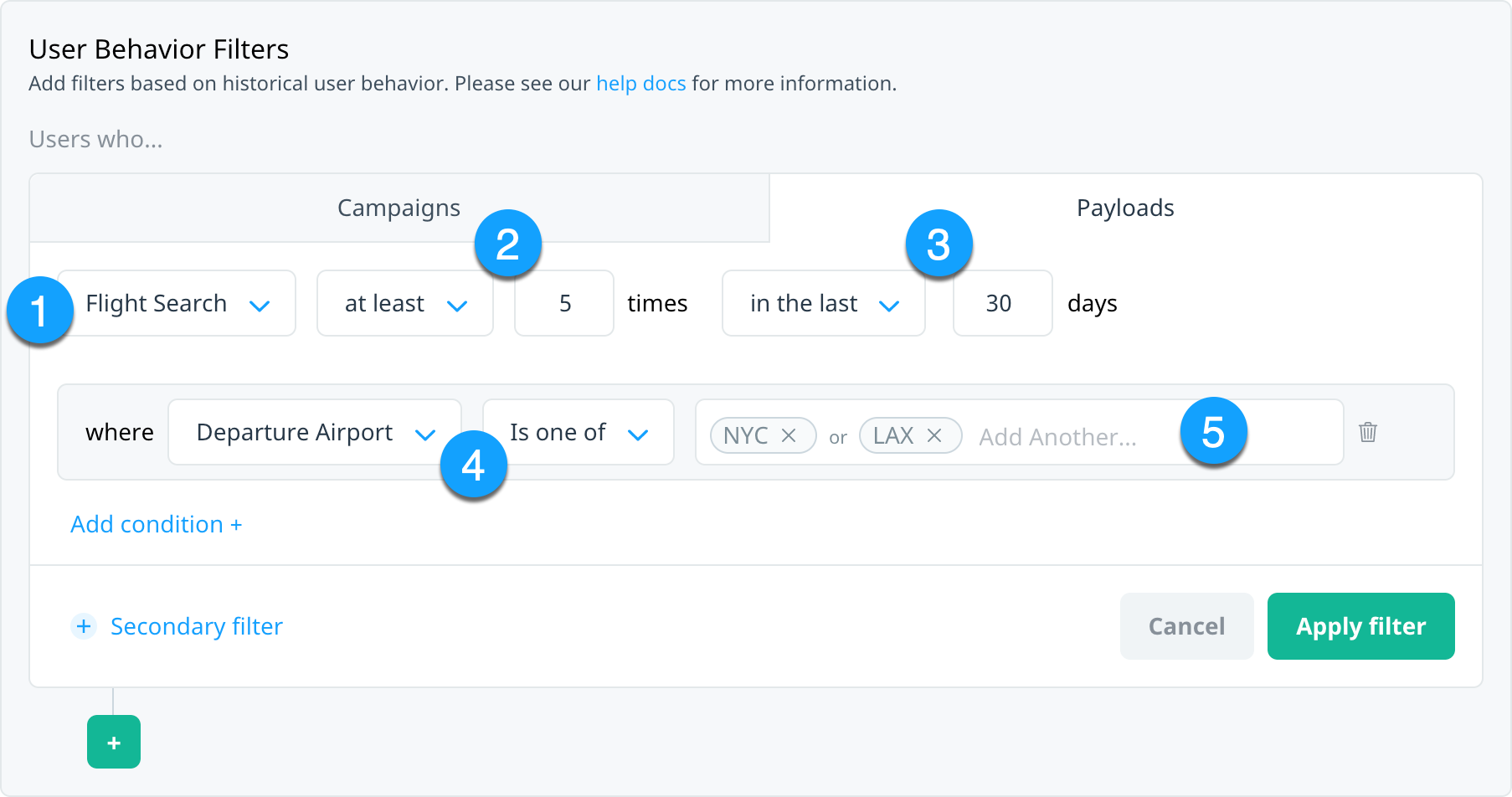
User behavior Payload filters include the following elements:
| Element | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | event | This is the top-level event reflecting the user action you want to use to target your audience. For an event to be displayed in this list, your Customer Success Manager must specifically configure it for behavioral targeting (see Prerequisites). In this example, we’ll use an event called Flight Search. |
| 2 | event frequency and count | The number of times the user has triggered the selected event. For example, the user has searched for a flight at least 5 times. |
| 3 | event recency and time frame | The time frame over which to measure the frequency of the event. For example, in the last 30 days. |
| 4 | event payload | Any additional payload constraints you want to apply to the filter. For example, Destination Airport is one of. |
| 5 | payload criteria | The payload values you want to use to target your users. For example, if your payload is Destination Airport, this could be a list of airport codes. Enter the values as free text. |
The following sections describe the operators that are available for each element.
Event frequency
The event frequency operators are applied with the other filter constraints (that is, the time frame and payloads).
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| exactly | Matches users who triggered the event exactly X times, where the number of times is greater than or equal to zero. |
| at most | Matches users who triggered the event at most X times, where X>0. |
| at least | Matches users who triggered the event at least X times, where X>0. |
| between | Matches users who triggered the event between X and Y times. The range is inclusive. |
| not between | Matches users who triggered the event not between X or Y times. That is, less than X and more than Y. The range is exclusive. |
Event recency
The event recency operators determine the time frame over which to measure the event frequency and associated payloads.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| anytime | Matches the event count and payload values for anytime in the history of the app (that is, since the app started logging events in Swrve). |
| in the last | Matches the event count and payload values in the last X days. |
| more than | Matches the event count and payload values more than X days ago. |
| between (days ago) | Matches the event count and payload values between X and Y days ago (inclusive). |
| between (dates) | Matches the event count and payload values between two specific dates, specified in UTC. The time range defined by the two dates is inclusive of the start and end dates specified. |
Event payloads
After you select the event frequency and recency, select Add condition + to add payload conditions to the filter. The event payload list only displays the payloads that are included in the event configuration. If a payload you want to target is not displayed in this list, contact your CSM at support@swrve.com.
You can include up to a maximum of 20 payloads per event for targeting purposes. Depending on the type of data, each payload is configured as a type—string, integer, date, or float—which determines the operators that are available when using that type of payload.
String payloads
If an event payload is configured as a string, the following operators are available. Matching payloads values can contain spaces and are not case sensitive.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| Is one of | Matches users where the payload value is one of a list of potential values. You can include one or more values in the list. |
| Is not one of | Matches users where the payload value is not one of a list of potential values. |
| Contains | Matches users where the payload value contains the specified string. |
| Starts with | Matches users where the payload value starts with the specified string. |
| Ends with | Matches users where the payload value ends with the specified string. |
Integer payloads
If an event payload is configured as an integer (that is, a whole number), the following operators are available.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| Is | Matches users where the payload value is exactly the specified value. |
| Is not | Matches users where the payload value is not the specified value. |
| Is less than | Matches users where the payload is less than the specified value. |
| Is greater than | Matches users where the payload is greater than the specified value. |
| Is between | Matches users where the payload falls within the range of the specified values. The range is inclusive. |
| Is not between | Matches users where the payload falls outside the range of the specified values. The range is exclusive. |
Date payloads
If an event payload is configured as a date, the following operators are available. Note: For targeting purposes, one day equals a 24-hour sliding window from the point of evaluation.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| Is on | Matches users where the payload is a specific date, in UTC. |
| Is (future) | Matches users where the payload date is a specific number of days in the future, as measured from the point when the audience is calculated. |
| Is (past) | Matches users where the payload date is a specific number of days in the past, as measured from the point when the audience is calculated. |
| Is between dates | Matches users where the payload date falls within the specific range of dates (inclusive). |
| Is not between dates | Matches users where the payload date falls outside the specified range of dates (exclusive). |
| Is between | Matches users where the payload date falls within the range of the specified number of days in the past, relative to the point when the audience is calculated. |
| Is not between | Matches users where the payload date falls outside the range of the specified number of days in the past, relative to the point when the audience is calculated. |
Float payloads
If an event payload is configured as a float (that is, a number that can include decimals), the following operators are available.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| Is less than | Matches users where the payload is less than the specified value. |
| Is greater than | Matches users where the payload is greater than the specified value. |
| Is between | Matches users where the payload falls within the range of the specified values. The range is inclusive. |
| Is not between | Matches users where the payload falls outside the range of the specified values. The range is exclusive. |
Filter combinations
This section shows you how to combine multiple events or multiple payloads to target your audience.
By default, the primary operator is OR and the secondary operator is AND. When the primary operator is:
- OR – targeted users can match any of the selected filter groups. Within each group, you can specify additional AND filters.
- AND – targeted users must match all of the selected filter groups. Within each group, you can specify additional OR filters.
Switching the primary filter or secondary filter automatically changes the operators to the opposite configuration (that is, from AND to OR, and, from OR to AND).
Primary filters
To create a new filter group, outside the filter group select Add a new filter , which adds a primary operator to your filter definition.
When the first filter in the group is in edit state
When you’ve applied a single filter
When you’ve added multiple filters within a group
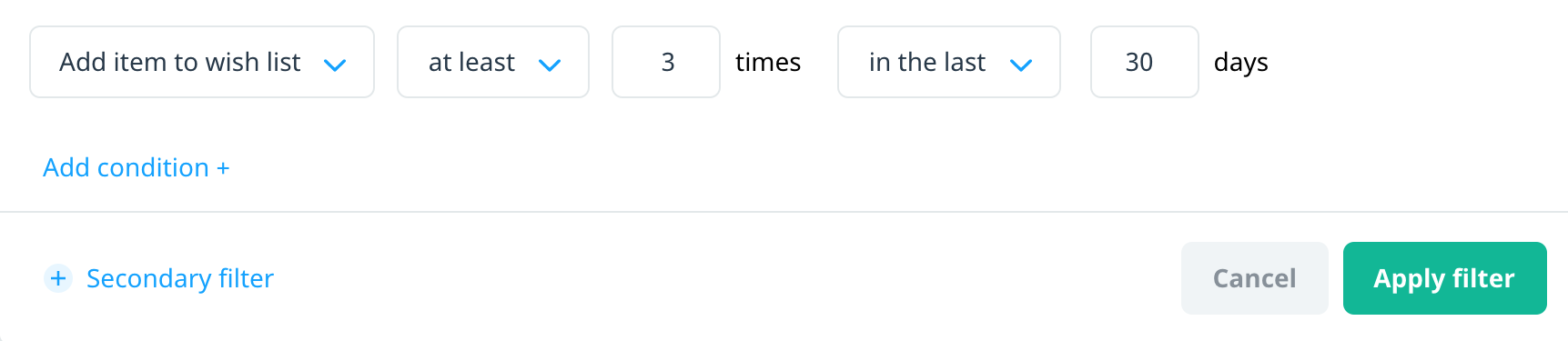
Secondary filters
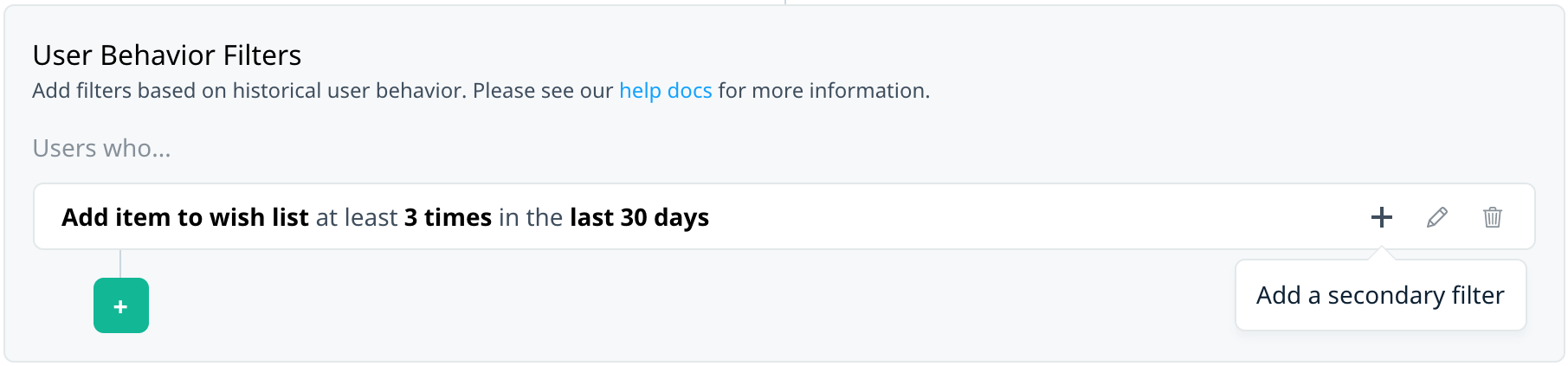
To create more complex filters, use a secondary filter to apply additional constraints within a filter group. The option for adding a secondary filter changes depending on whether or not the group already has a filter.
First secondary filter
To add a second filter within a group while editing a filter, select + Secondary filter.
To add a second filter within a group after applying the first filter in the group, select Add a secondary filter on the summary bar.
Subsequent secondary filters
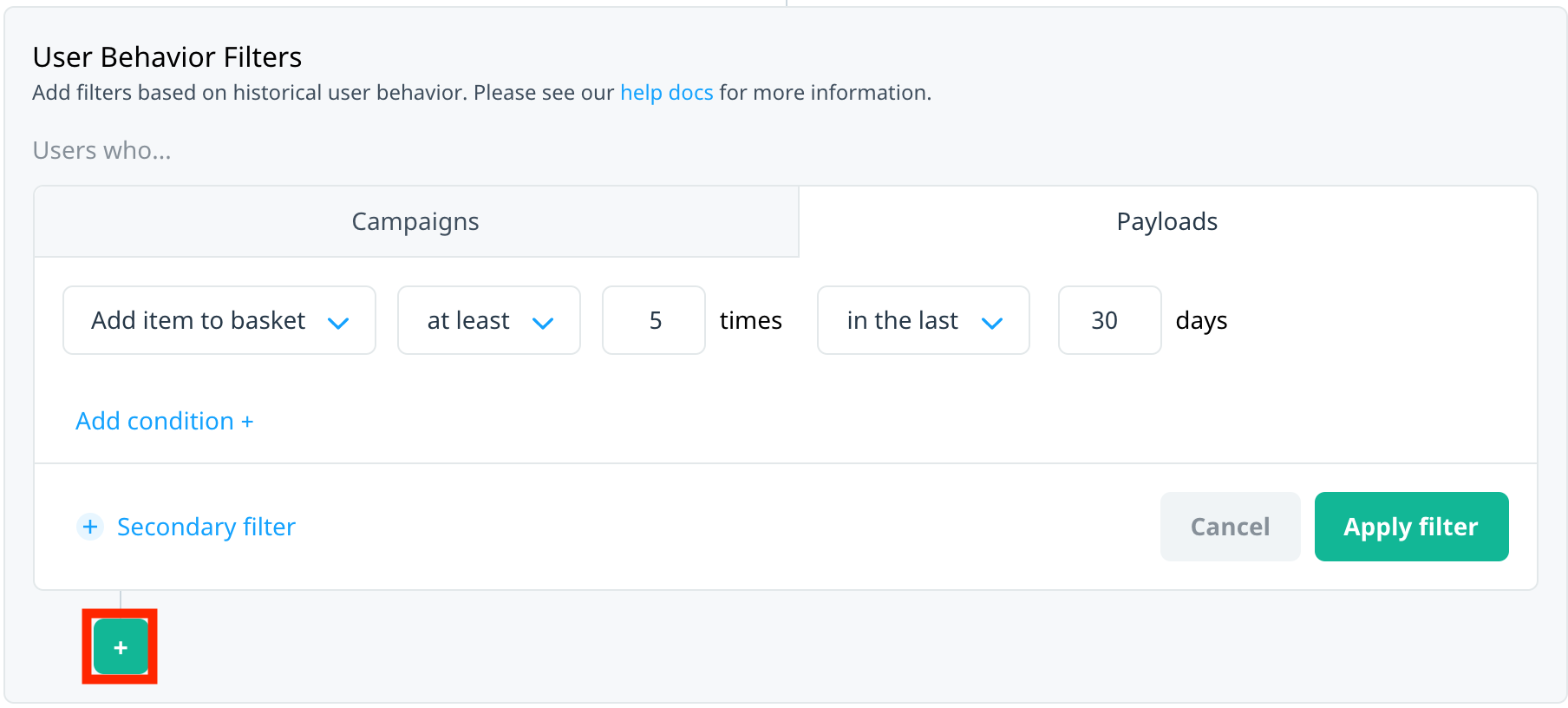
Once a group has multiple filters, to create additional secondary filters, select Add secondary filter in the filter group
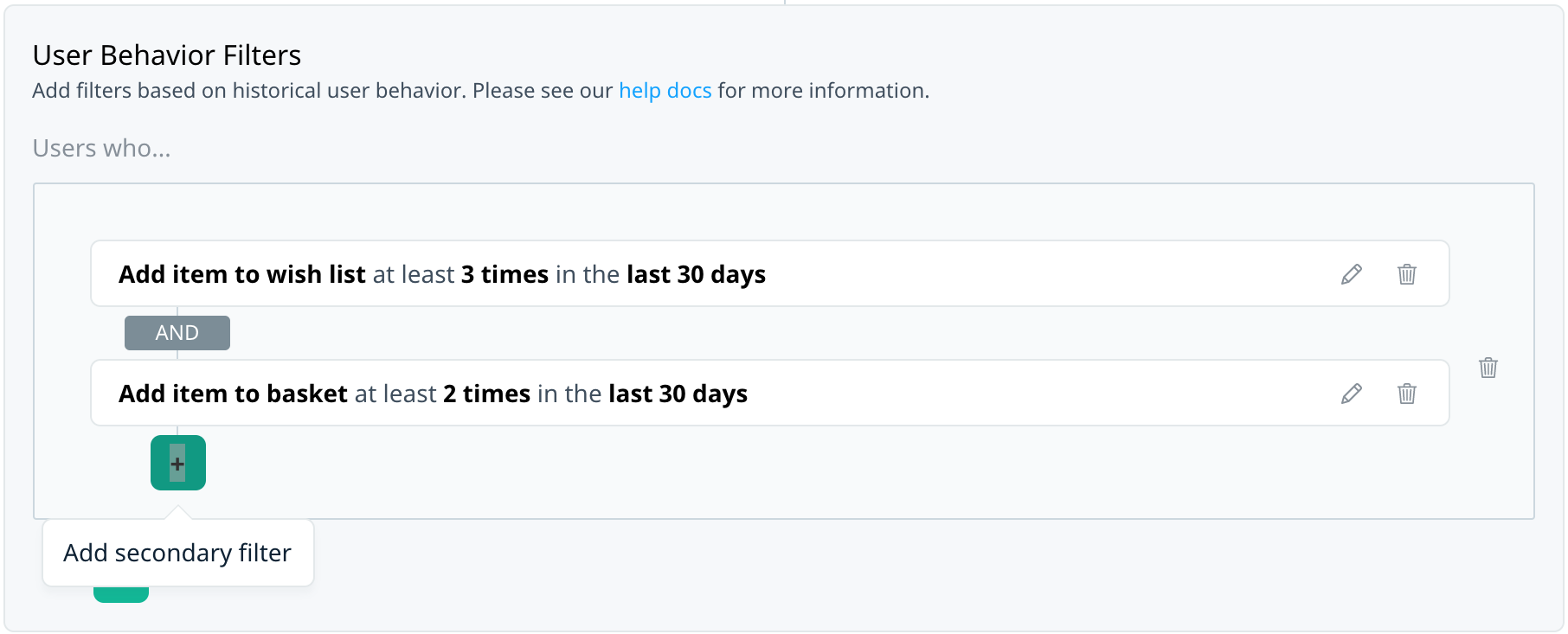
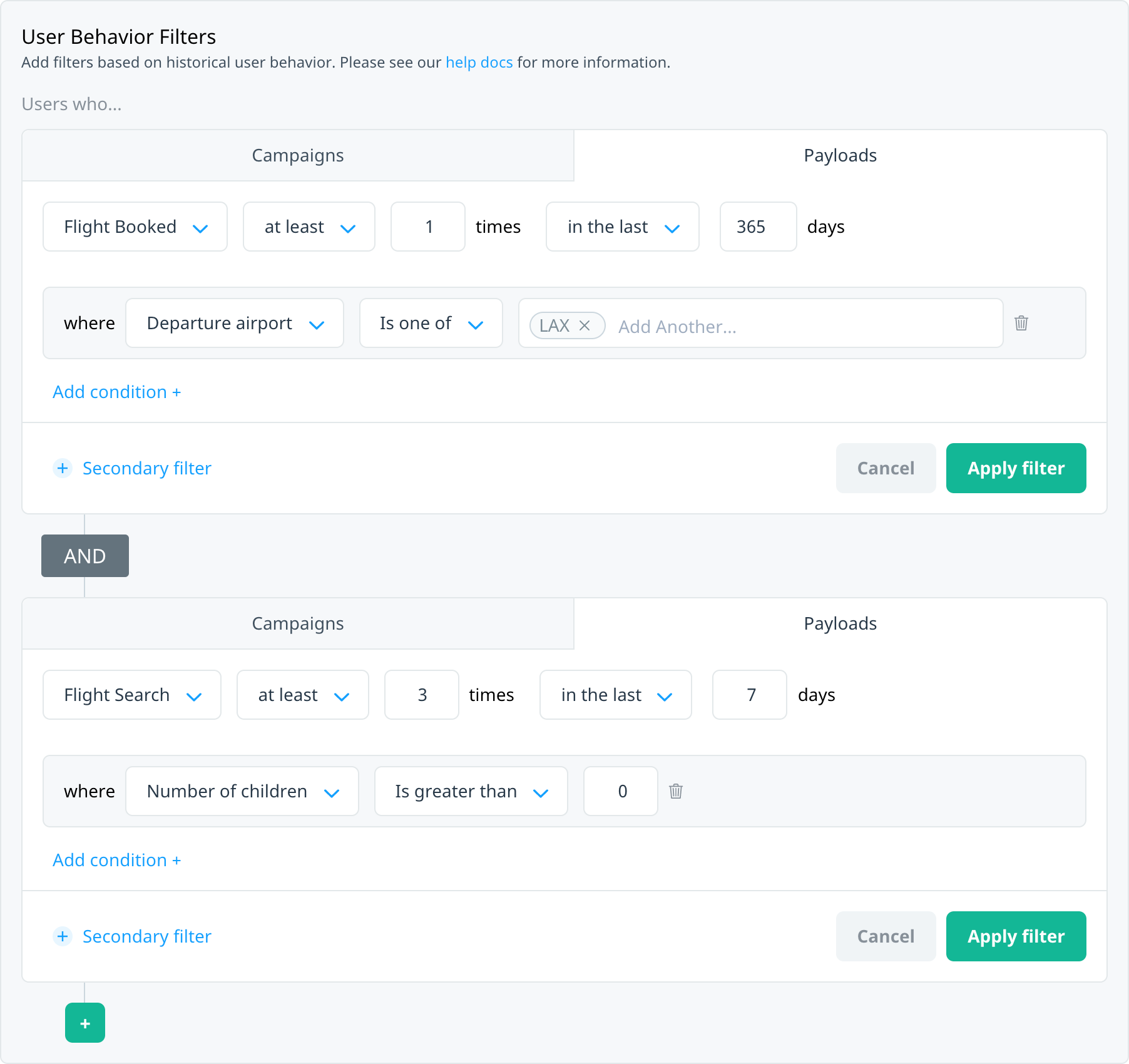
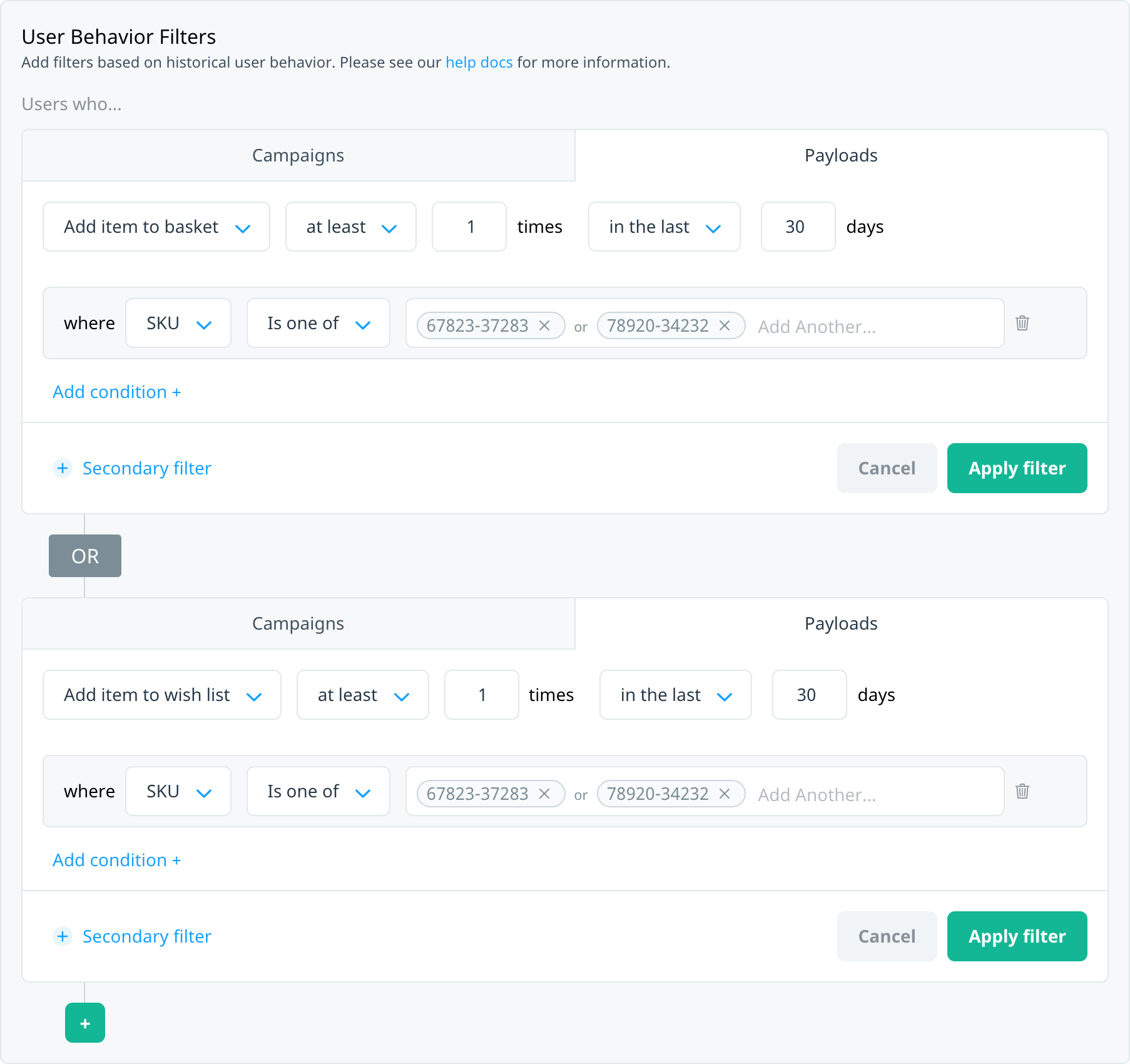
Multiple events
Use the AND/OR operator to create filters where your users must match all events (AND) or match one of several events (OR). There is no limit to the number of events you can include.
Match all events
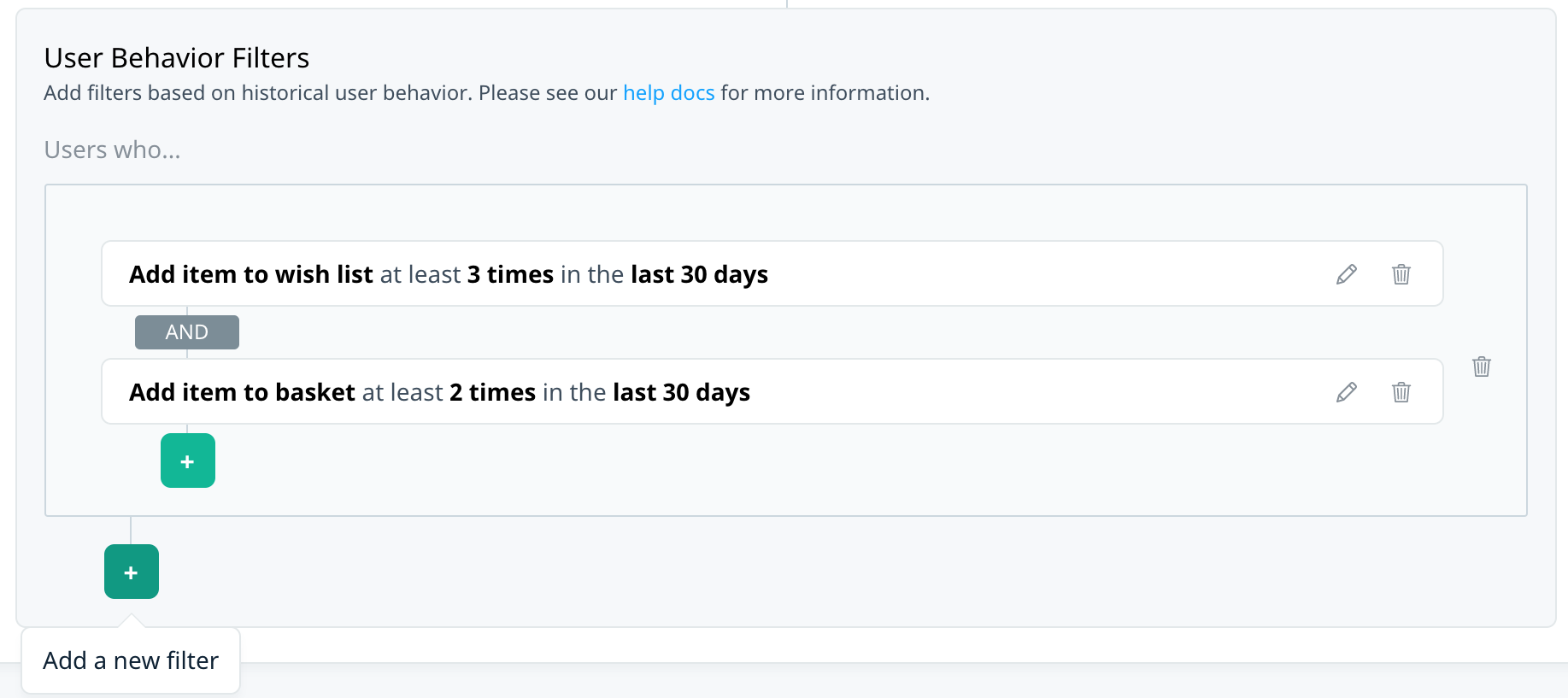
Target users who match multiple events, each with their own set of criteria. For example, target users who booked a flight from LAX in the last year and recently performed a flight search that included children in the number of travelers.
Match any events
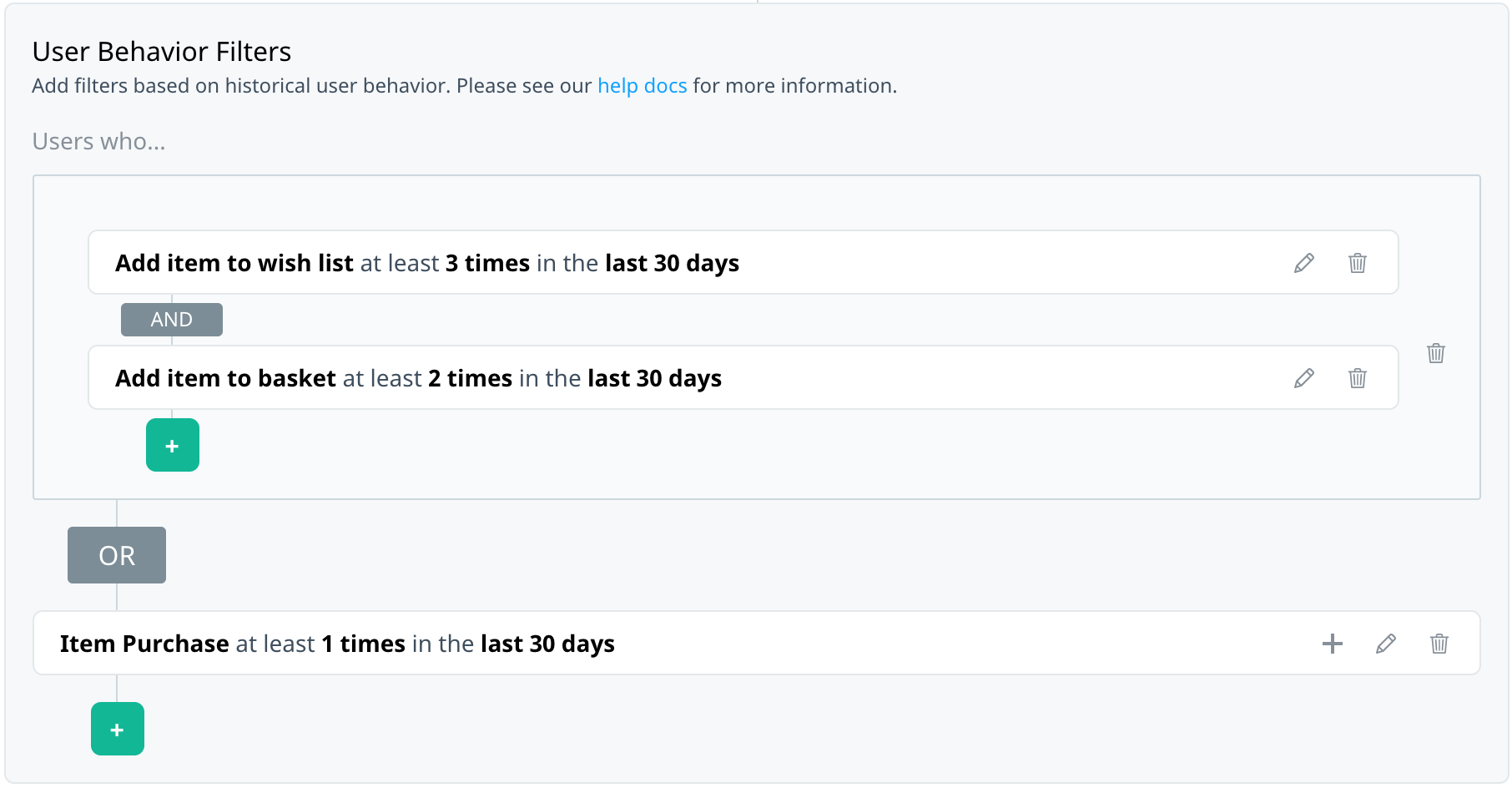
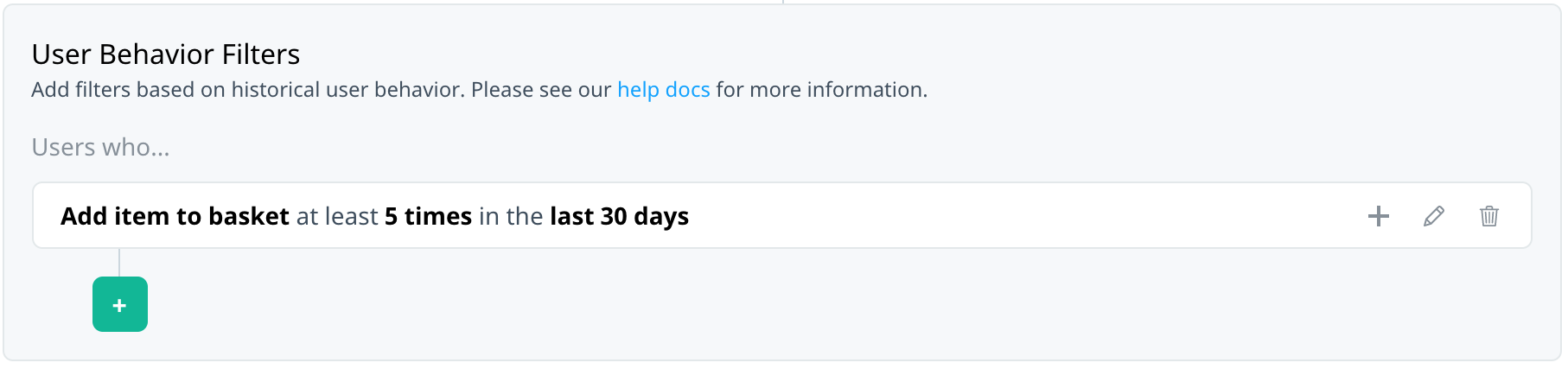
You might be interested in users who match one of several events, each with their own set of criteria. For example, target users who recently added a specific item to their basket or wish list.
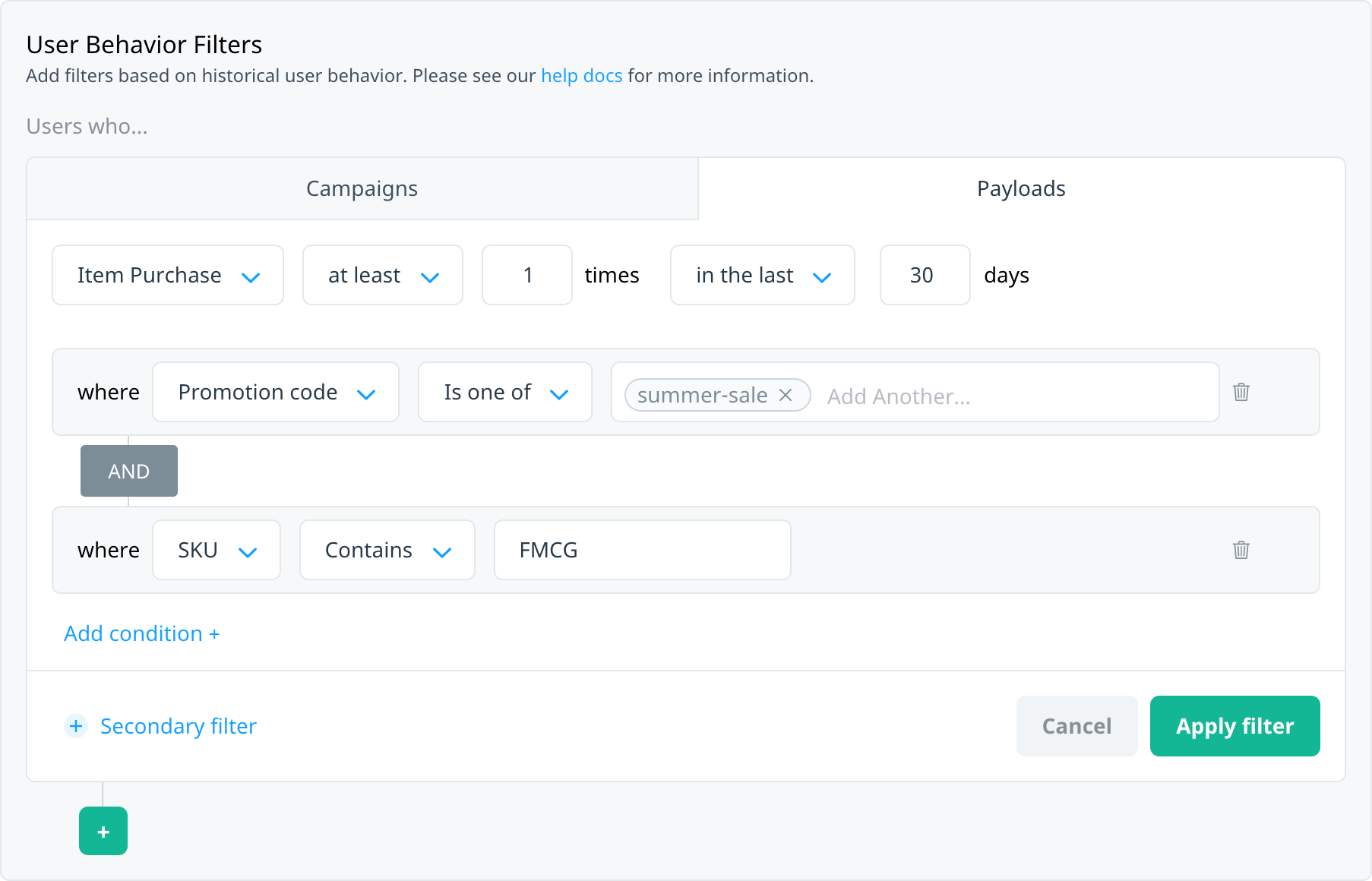
Multiple payloads
Within each event, use the AND/OR operator to add multiple payload criteria to the same event. To add another payload filter to an event, select Add condition. Select the operator to switch between AND and OR.
Match all payloads
You might want to include multiple payload filters on an event and require that users match all of them to qualify for the target audience. For example, target users who made a purchase using a “summer-sale” promotional code and an SKU containing “FMCG”.
Match any payload
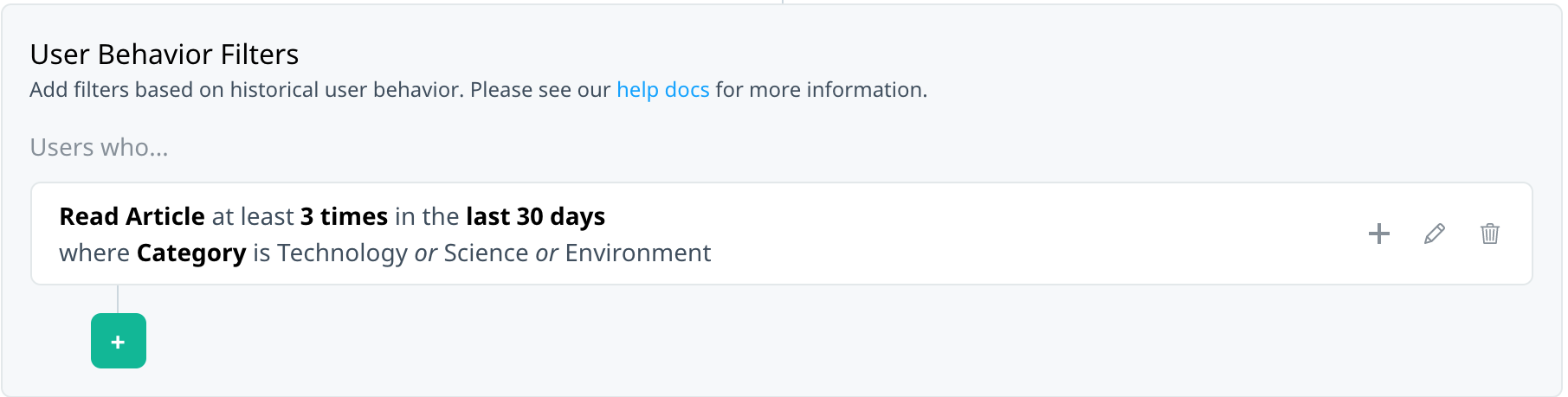
You might want to include multiple payload filters on an event and require that users match any of them to qualify for the target audience. For example, target users who read at least three articles in the last month in the Technology category or with a title that starts with “Tech Review”.
Targeting recent event frequency
You might want to target your users based on the frequency of an event without including payload criteria, as the following examples show.
Targeting custom events
Target users who searched for any flight at least five times in the last month:
Target users who made at least one purchase in the last six months:
Target users who watched at least 10 shows in the month of August:
Targeting session events
Use session events to target users based on their recent session frequency. To have your custom events configured to include session recency, contact your CSM at support@swrve.com.
Target users who had at least three sessions in the last seven days:
Target users who had between 3 and 10 sessions in the month of August.
Saving audience filters
After you’ve added the required user behavior filters, to save the audience to your campaign, select Apply filters. A summary of the filter is displayed. Edit or add to the filter as needed.
The following actions are available on the filter summary:
- Select edit to make changes to the existing filter.
- Select delete to remove the existing filter.
- Select add to add another filter.
Audience estimates and other considerations
As you select filters for your audience, the estimated target audience is displayed in the top right of the audience builder. For a user to be included in the target audience, they must meet all of the criteria for the selected elements, so it’s important to understand how the filter operators and event processing rates may affect the audience that is returned.
Negative definitions
If you try to target your audience based on a negative definition, for example, “[payload] is not [payload value]”, the system only returns users who are already in the payload targeting system. That is, they must first have triggered the event or have the payload value set that you’re trying to target to qualify for the audience.
Swrve processes user profile properties and user behavior event payloads at different rates. If you target your audience with a negative user profile filter, for example, “[user property] is not [property value]”, there is a possibility a new user could be included in the payload targeting system but not have an updated user profile property at the time the audience is calculated, and incorrectly get included in the target audience. To avoid this, use the AND operator to add another filter that includes a positive match against another property.